DAX Studio
Here are a few things that you can do.
1.
Extract a list of your measures from your data
model into a spreadsheet
·
for looking at the big picture
·
for documentation
·
so you can more easily reuse the measures in another workbook
without having to go hunting for them
2.
Help you write more complex DAX formulas that
contain “tables” as part of the formula.
·
When you write a measure that contains a table function in DAX,
you can’t actually “see” the table to check if it is returning the table
you expect. In DAX Studio, you can write just the Table portion of your
formula so you can actually “see” the table that is produced. This makes
it a lot easier to work out what you are doing, work out what is wrong, and
hence solve problems you are having when writing formulas.
3.
Learn how to write DAX Queries
·
It may not be immediately obvious, but once you build lots of
business logic into your data model, there could be times when you just want to
get a table (or list) of data and extract it to use for other purposes. You could use a pivot table for this, but it can be better to
write a query over the data model and extract the data you need into a table in
some instances – particularly if the table is large.
4.
Test performance of your measures
·
When a measure (eg in a pivot table) is really slow, you can run
the measure in DAX studio and use the server timing tools to see how Power
Pivot is interpreting your formula. With this information you can set
about re-writing the formula to be more efficient.
5.
Use a Power BI Desktop PBIX file as a SSAS
Server (kind of)
·
There is a trick that allows you to use Power BI Desktop as a
server and then connect a thin Excel Workbook to this “server”. It only
works for the life of the session, but it is still cool and could be useful.
It is important to note that DAX Studio ALWAYS returns a
Table – there is no other choice. This is exactly opposite to
a measure in a pivot table which ALWAYS returns a scalar value. You can
use this fact to your advantage to help you debug measures that contain tables
as part of the formula (which is hard to do in a measure/pivot table).
And there is a trick to allow you to return a single measure scalar value as a
table – more on that later.
The latest version of DAX Studio can be downloaded here.
Connection:
DAX Studio to Power BI Desktop
You can however launch DAX Studio from your Program Files from within Windows. If you have Power BI Desktop open when you launch DAX studio, you will get a connection dialogue as shown below. Just select the correct data model for the open Power BI PBIX file.
Note: You can also use DAX Studio to connect to SQL Server Tabular.
There is a lot to DAX Studio, few things in the UI to get you started (Referring to the image below).
- This is the list of tables in your data model – it should be familiar to you
- This is the query pane – it is where you write your queries
- This is the run button to execute your query (you can also press F5).
- This is the default output pane – where you will see the results of your query
- You can change the default output from the output pane (4) to various other alternatives including Excel or a file (CSV or TXT).
- Once you write your query in the query pane (2), you can click this button to use the DAX Formatter service to format the query directly in the query pane so it is easier to read.
- The server timings button is used for performance testing – more on that later
- The connect button allows you to repoint DAX studio to a different data model.
- Down the bottom of the page you can change from the list of tables to some of the other tabs including Functions (to help you write DAX) and DMV (Dynamic Management Views). DMVs are a set of technical queries that will return you information about your data model. More on that later too.

Measures
The first thing I am going to cover is how to extract a list of measures from your workbook. There is a DMV for measures that is really easy to use. Simply do the following:
- Down the bottom of the DAX Studio window, click on the DMV tab.
- Scroll down the list of DMVs and find MDSCHEMA_MEASURES towards the bottom of the list.
- Click and drag the DMV and drop it in the Query Pane window as shown below.

When you do this, DAX Studio will automatically write your first query for you (shown as 1 below). NB: This is not a DAX query but a SQL query. You can then run the query by pressing the run button (2) or better still just get used to pressing F5.

Take a look at what you get down the bottom of the screen in the Output tab (1 below) and the Results tab (2 below).

The results tab (shown below) is simply a temporary storage location for the table returned by DAX Studio. In fact the resulting table from this DMV is too large to fit on the screen (but you can use the scroll bars to see the rest of the table).

It is possible to change the output location to Excel as follows. At the top of DAX Studio, change the default output (shown as 1 below) to Excel Static (2 below).

Once you run the query again (press F5) the results get sent to your Excel Workbook. There is a lot more information provided in the output than you are likely to need. In my sheet below I have only kept columns D and N. Note how the first 14 rows in my model are not useful, but from row 15 you can see a list of the measures and formulas. Very helpful for documentation and also for copying measures to other workbooks.

Now you can manually delete the columns and rows you don’t need to create a nice clean list of measures, but why not download and install Power Pivot Utilities like I mentioned earlier. Power Pivot Utilities uses DAX Studio in the background to extract the measures (and other things) automatically for you, clean up the list and put it in a worksheet which is all nicely formatted – much easier. You must have both Power Pivot Utilities and DAX Studio installed for this to work.

- Click on the PP Utilities menu (shown as 1 above).
- Click “List Measures” (shown as 2 above), you will get this.

Then why not go one step further. Select (highlight) the DAX Formulas in the table that you want to format, then click “Format DAX expressions”, then you will get this – super!

here is a small SQL script that you can cut and paste into the DAX Studio query window and get a tight extract of just the measures.
from $SYSTEM.MDSCHEMA_MEASURES
where MEASURE_AGGREGATOR = 0
order by MEASUREGROUP_NAME
Extracting an Existing Table
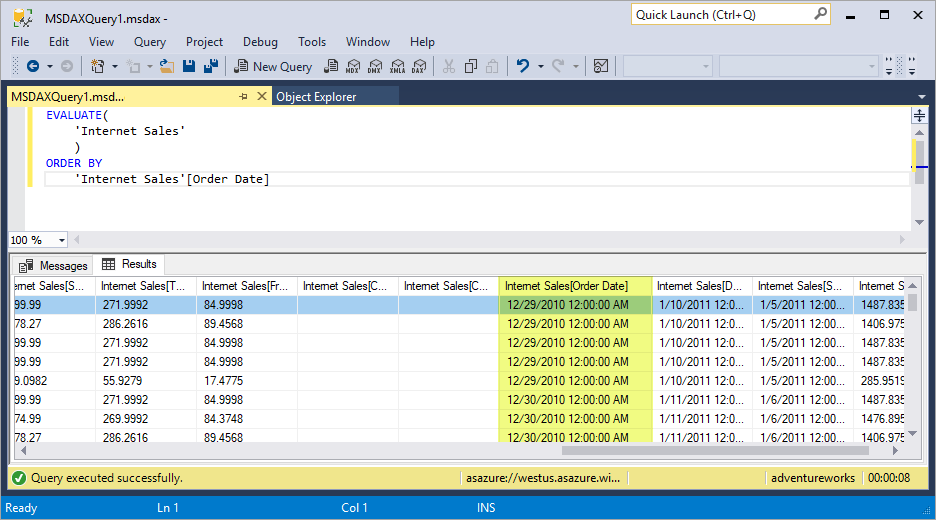
Every DAX Query must start with the EVALUATE keyword. The query below simply uses EVALUATE followed by the name of one of the tables (Product in this case). It is good practice to use line breaks in the query pane to make your DAX Query easier to read. DAX studio has very good Intellisense, code highlighting, and you can also use the tab key to space out your queries.
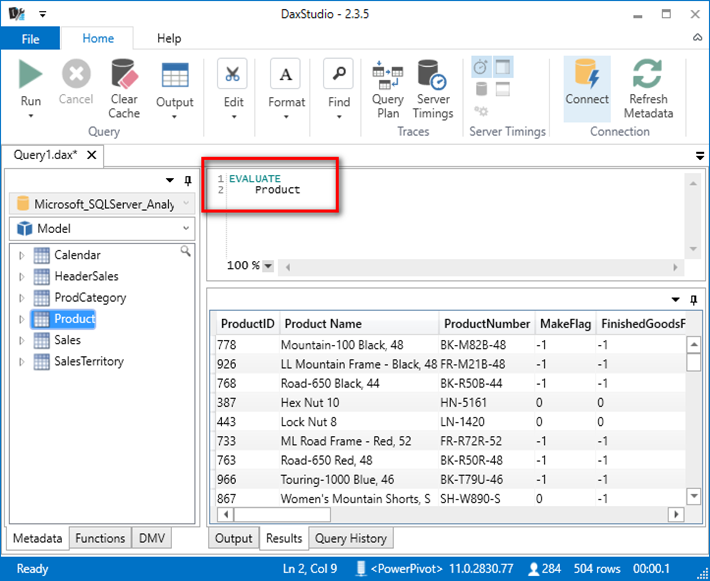
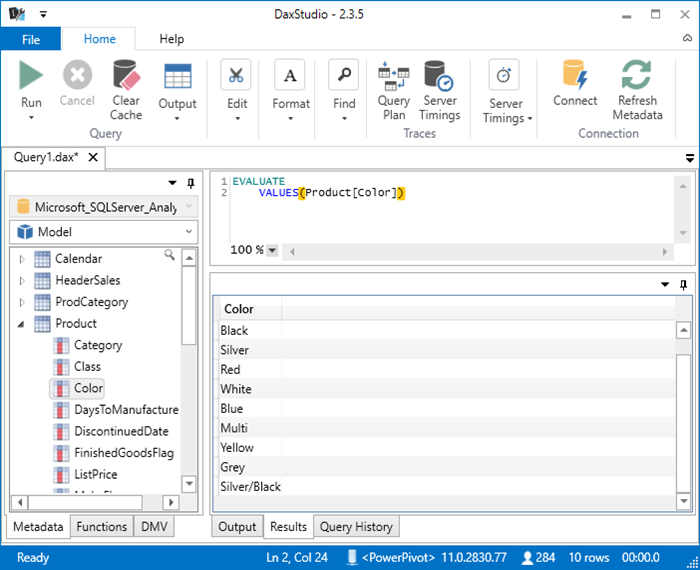
There are a number of regular DAX functions that return Tables including FILTER, VALUES, CALCULATETABLE, DATEADD...
the same can be done with the FILTER function. Below I extract a list of all Products that have a list price of $1,000 or more.